Tindakan Medis & Terapi
CT Calcium Score: Procedure, Interpretation, Cost & Ways to Lower It
Written By
Admin TzuChi • 04 November 2025
This article explains the CT calcium score procedure, how to interpret your score, the causes of high results, and ways to lower your risk.
What Is a CT Calcium Score?
A CT calcium score is a heart CT scan that detects calcium deposits in the coronary arteries.
Calcium buildup usually indicates artery hardening caused by plaque, which increases the risk of heart disease and heart attacks.
While calcium is essential for heart rhythm and blood pressure regulation, it can get trapped in damaged arteries and cause stiffening, leading to coronary artery disease.
When Should You Get the Test?
Not everyone needs a CT calcium score. It’s generally recommended for people with heart disease risk factors, such as:
-
Age between 40–70 years
-
History of high blood pressure
-
History of high cholesterol
-
Smoking habit
If your risk is too low or too high, the test may not be useful since it only adds unnecessary radiation exposure.
Who Should Avoid the Test?
In some cases, a CT calcium score is not recommended due to radiation exposure or limited usefulness. It’s not suitable for:
-
Pregnant women (radiation can harm the fetus)
-
People without heart disease risk factors
-
Patients already diagnosed with coronary artery disease
-
Individuals with heart symptoms (other diagnostic tests are better)
-
Those monitoring heart treatment effectiveness
-
Extremely obese individuals who may exceed scanner limits
Calcium Score Procedure
The test is quick—around 10–15 minutes—and doesn’t require contrast dye.
1. Preparation
Avoid caffeine or smoking 4 hours before the test. You’ll be asked to remove jewelry and upper clothing and wear a hospital gown.
2. Electrode Placement
Electrodes are attached to your chest to monitor heart activity during the scan. Some patients may receive medication to help relax or lower their heart rate for clearer images.
3. Scanning Process
You’ll lie on a table that slides into the CT scanner. The scan takes only a few seconds. During the process, you may be asked to hold your breath for 10–20 seconds.
4. After the Test
You can go home immediately. A radiologist will analyze the images and calculate your calcium score, which estimates plaque buildup and coronary artery disease risk.
Possible Side Effects
The test is painless but may feel uncomfortable because you must stay still in a confined space.
Radiation exposure is minimal, and the chance of cancer risk increase is extremely low.
CT Calcium Score Cost
The cost is relatively affordable—usually under Rp1 million, and even cheaper during promotions.
However, not all insurance plans cover this test, so check beforehand.
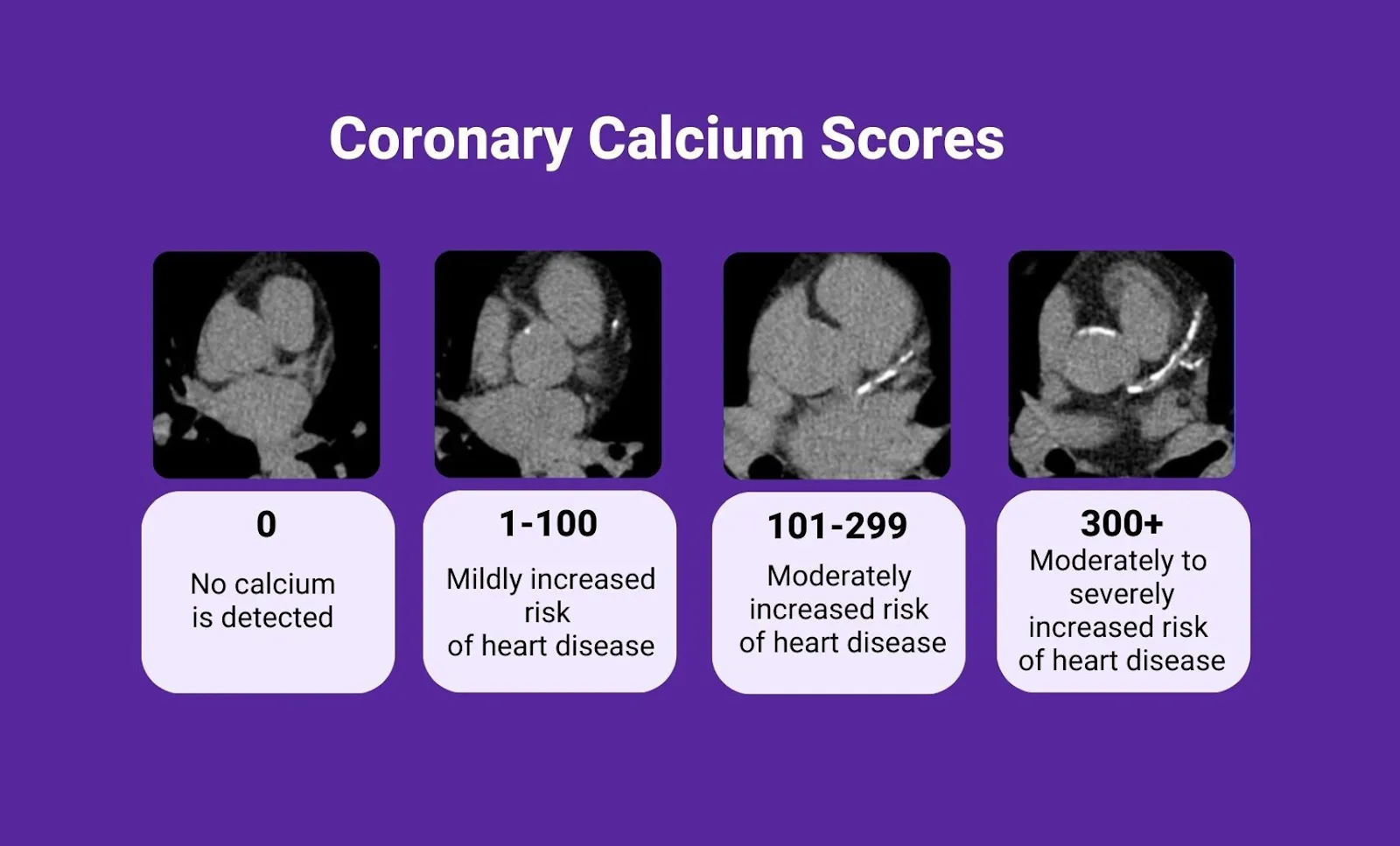
Calcium Score Results and Interpretation
| Calcium Score | Meaning | Heart Disease Risk |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | No calcium plaque | Very low risk (<1% in 7–10 years) |
| 1–10 | Minimal plaque | Low risk, early atherosclerosis |
| 11–100 | Mild plaque | Moderate risk, lifestyle changes recommended |
| 101–400 | Moderate plaque | Moderate to high risk, may need medication (e.g., statins) |
| >400 | Extensive plaque | High risk, treatment required |
A score of 0 is considered ideal. However, a slightly higher score can be normal in older adults.
A high score doesn’t always mean an imminent heart attack but indicates the need for preventive care.
Causes of High Calcium Score
A high calcium score occurs due to plaque buildup (atherosclerosis) in coronary arteries.
Plaque forms from fat, cholesterol, and other substances that stick to artery walls. Over time, this hardens due to calcium exposure—called coronary artery calcification—which restricts blood flow and increases heart disease risk.
How to Prevent Higher Calcium Scores
If your score is high, doctors may suggest:
-
Consulting a cardiologist
-
Taking statins or other medications to reduce plaque buildup
-
Exercising regularly
-
Limiting saturated fats and sugar
-
Routine heart check-ups to monitor calcium progression
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Is CT calcium scoring the same as a regular CT scan?
No. Calcium scoring uses CT technology specifically to detect calcium in the coronary arteries.
Why use a heart CT scan?
It provides detailed coronary artery images quickly, non-invasively, and accurately.
Is it safe?
Yes. The procedure is safe, painless, and involves very low radiation exposure.
When Should You See a Doctor?
If you have risk factors like high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, or a family history of heart disease, consider a CT calcium score.
Tzu Chi Hospital offers this test at its radiology unit using advanced heart CT scanners. It’s non-invasive, contrast-free, and can quickly detect calcium buildup in coronary arteries.
The hospital also features an international-standard Cath Lab for further cardiac procedures like angiography, stenting (PCI), and other catheter-based interventions.
With advanced tools such as Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) and Rotablator, Tzu Chi Hospital ensures comprehensive heart care—from early detection to treatment.
Schedule your appointment via WhatsApp Tzu Chi Hospital and check doctor availability through the Find Doctor feature.
Getting tested early helps prevent serious heart disease later.
This article has been medically reviewed by dr. Hendra Simarmata, Sp.JP(K), FIHA
Topic





